Scatter Plot: An Assumption of Regression Analysis
What is the value in examining a scatter plot for a regression analysis?
Residual scatter plots provide a visual examination of the assumption homoscedasticity between the predicted dependent variable scores and the errors of prediction. The primary benefit is that the assumption can be viewed and analyzed with one glance; therefore, any violation can be determined quickly and easily. When an analysis meets the assumptions, the chances for making Type I and Type II errors are reduced, which improves the accuracy of the research findings.
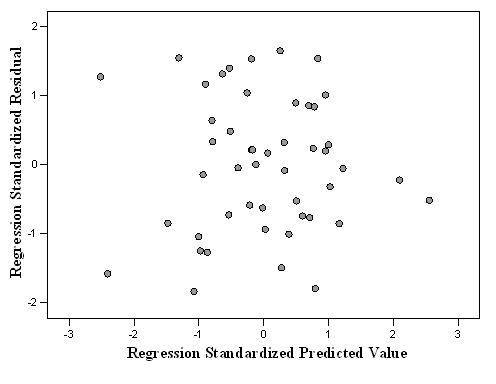
A residual scatter plot is a figure that shows one axis for predicted scores and one axis for errors of prediction. Initial visual examination can isolate any outliers, otherwise known as extreme scores, in the data-set. Tabachnick and Fidell (2007) explain the residuals (the difference between the obtained DV and the predicted DV scores) and the variance of the residuals should be the same for all predicted scores (homoscedasticity). If this is true, the assumption is met and the scatter plot takes the (approximate) shape of a rectangular; scores will be concentrated in the center (about the 0 point) and distributed in a rectangular pattern. More simply, scores will be randomly scattered about a horizontal line. In contrast, any systematic pattern or clustering of scores is considered a violation.
The figure below shows a random displacement of scores that take on a rectangular shape with no clustering or systematic pattern. The figure shows the assumption of homoscedasticity is met.
Regression help?
Option 1: User-friendly Software
Transform raw data to written interpreted results in seconds.
Option 2: Professional Statistician
Collaborate with a statistician to complete and understand your results.
*For assistance with regression or other quantitative analyses click here.
Reference
Tabachnick, B. G. & Fidell, L. S. (2007). Using multivariate statistics (5th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon. View
Related Pages: