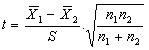Independent Sample T-Test
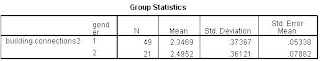
The independent samples t-test analyzes the mean comparison of two independent groups. When we take two samples from the same population, then the mean of the two samples may be identical. However, when samples come from different populations, their means may differ. In this case, it helps determine whether the population means are similar or different.
Assumptions:
1. It assumes the dependent variable follows a normal distribution.
2. Assumes that the variance of the two groups are the same as the dependent variable.
3. Assumes that the two samples are independent of each other.
4. It draws samples randomly from the population.
5. All observations must be independent of each other.
6. Dependent variables must be measured on an interval or ratio scale.
Need help conducting your Independent Sample T-Test? Leverage our 30+ years of experience and low-cost same-day service to complete your results today!
Schedule now using the calendar below.
Procedure:
1. Set up the hypothesis.
a. Null Hypothesis: It is assumed when the means of the two groups are not significantly different.
b. Alternative Hypothesis: Assumes that the means of the two groups are significantly different.
2. Calculate the standard deviation by using this formula:
V= degree of freedom
N1+N2= number of observations in both samples.
5. Hypothesis testing: Statistical decisions are made about whether or not the two population means are identical. Compare the calculated value with the table value. If the calculated value is greater than the table value of the predetermined significance level, we will reject the null hypothesis and say that the means of the two groups are different. If the calculated value of the is less than the table value, then we will say that the means of the two groups are the same.
SPSS:
2. Click on the “open data” icon and select the data.
3. Click on the “analysis” option and select “compare mean” from the analysis option.
4. Select “independent sample t-test” from the compare mean option, the following window will appear: